THEIR FUNCTIONS

Adenoids:
Often these organs are enlarged in children and obstruct nasal breathing.
Adrenal Glands:
Essential to life and for hormone secretions such as adrenalin,cortisone, etc. Regulates chemistry of essential body chemicals such as sodium, chlorides, potassium
Anus :
Is muscles control bowel evacuation.
Appendix:
It is a vestige of man’s primitive past.
Bladder:
Acts as reservoir for urine which has been excreted by kidneys.
Bone marrow:
Manufactures blood cells.
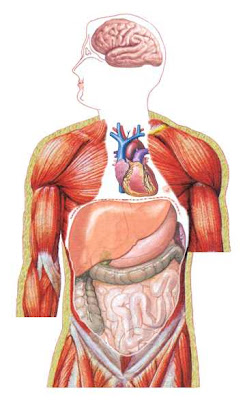
Brain:
Control of mental and nerve activities.
Bronchial tubes:
These are the tubes through which air moves in and out of the lungs.
Breasts:
In female, he breasts secrete milk, to suckle he babies.
Cervix of uterus:
Acts as barrier to infection; acts as passageway for sperm to enter uterus; dilates at childbirth to allow exit of unborn child.
Absorbs water from stool and propels stool on toward anus.
Duodenum:
Receives food from stomach and propels it on, receives bile from liver and gallbladder, receives digestive juices from pancreas, secretes digestive juices of its own.
Esophagus:
Transports swallowed food o stomach.
Fallopian tubes:
Transports egg from ovary to uterus. Fertilization of egg takes place within fallopian tube.
Gallbladder:
Stores and concentrates bile received from liver, and expels it into bile ducts, which carry it to intestinal tract.
Heart:
Pumps blood throughout body.
Ileum:
Absorbs food, absorbs water from intestinal contents, aids in digesting foodsl propels contents on to large intestine.
Jejunum:
Absorbs food, absorbs water from intestinal contents, aids in digesting foods propels contents onward.
Kidneys:
Filters excretes and reabsorbs and thus helps to control balance of blood constituents.
Larynx:
Controls act of speaking.
Liver:
Manufactures bile, controls metabolism of proteins, stores fat and sugar and purifies the blood.
Lungs:
These are the organs of respiration. They extract oxygen from air which is inhaled and they get rid of carbon dioxide with air which is exhaled.
Ovaries:
Produce an egg each month which, when fertilized, forms an embryo. Ovaries manufacture female hormones which are secreted into blood stream.
Pancreas:
Manufactures insulin, which controls sugar metabolism. Manufactures juices which help to digest foods.
Parathyroid glands:
Manufacture a hormone which controls metabolism of calcium and phosphorus.
Penis:
Male organ of intercourse. This organ acts as conveyor of urine from bladder.
Pharynx:
Commonly called the throat, it is the passageway for food and drink and also for air which is breathed.
Pituitary gland:
A most important gland whose hormone secretions, directly or indirectly, control metabolism. It is responsible for growth and for proper thyroid, adrenal and ovarian gland function.
Prostate gland:
I secrets fluid in which sperm are transported during ejaculation.
Pylorus:
Its strong muscle fibres regulate outflow of stomach contents into duodenum.
Rectum:
It conveys stool toward outlet of intestinal truct.
Seminal vesicles:
Store semen for discharge through the ejaculatory ducts when orgasm takes place.
Spinal cord:
This structure contains the nerves which travel from and to the brain and thus are responsible for sensation and movements.
Spleen:
In he unborn child, it manufactures blood cells. In the fully formed human, it destroys old, worn-out blood cells.
Stomach:
It churns undigested food and initiates digestion. It manufactures hydrochloric acid which helps to break down large food particles.
Testicles:
They manufacture sperm which are conveyed by the vas deferens to the seminal vesicles. They secrete male sex hormone into blood stream.
Thymus gland:
After the second year of life it degenerates. Nothing is known about its function.
Thyroid gland:
Manufactures the hormone, thyroxin, which controls metabolism.
Tongue:
This is an organ of taste. This helps in chewing and swallowing. This helps in the act of speaking.
Tonsils:
Function unknown.
Trachea:
Conveys air into and out of lungs.
Ureters:
Conveys urine from bladder to outside.
Uterus:
The organ in female womb within which the embryo develops.
Vagina:
The female organ in intercourse leading to the cervix. It is also through this canal that the newborn child is delivered.


No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.